Guide to Screening Test Services
Lab for Veterinary Cancer Care
Lab for Veterinary Cancer Care
Chemotherapy response prediction test
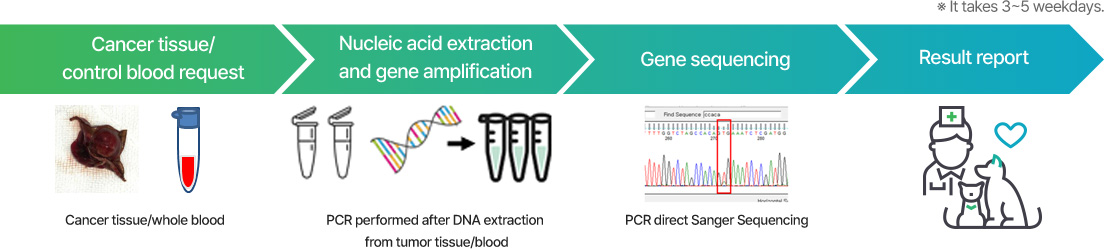
This is a test to select drugs predicted to have the most effective anti-cancer effect by comparing the anticancer effects of candidate anticancer drugs in animal cancer patients that need to undergo medical anticancer treatment after surgery.
In the test, cancer cells are isolated from surgically removed cancer tissue, cultured, and treated with 5 candidate anti-cancer drugs to compare the effect of killing cancer cells.
A veterinarian can select the drug with the best effect among the recommended candidate anticancer drugs, and use it for treatment under clinical judgment.
BRAF mutation hotspot test (first visit)
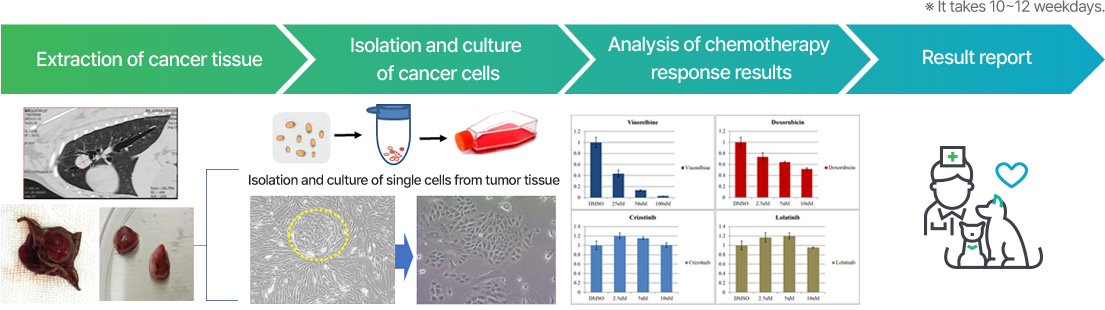
This is an auxiliary molecular diagnostic test that can be used when a malignant tumor is suspected in a companion dog's bladder, urethra, or prostate.
Mutation of the BRAF gene is detected in about 80% of transitional cell carcinomas in companion dogs, and as it is known as a causative gene for malignant tumors, it can be used as one of the companion cancer diagnostic tools. The presence of mutations in the BRAF gene that cancer cells can express is tested by using a companion dog’s urine and blood. The test can be performed with tissue from surgery or biopsy.
BRAF mutation hotspot test (revisit)
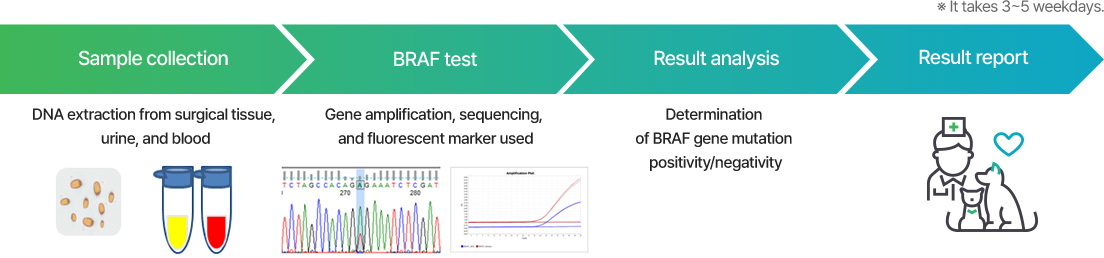
This test can be used to determine the treatment response and recurrence in patients confirmed to have a BRAF mutation among companion dog patients with malignant tumors.
It is possible to compare whether mutations are quantitatively increased or decreased by using consecutive samples from the same patient.
Gene mutations are tested using the dog’s urine, and thus please provide a blood sample for comparison.
BTA (Bladder Tumor Analytes) test
This is one of several diagnostic tests for cancers occurring in the urinary system of companion animals, and it uses latex agglutination reaction in a urine sample.
It can be used for the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma, but it can also be positive if inflammation, stone (calculus), or other infection findings are present in the bladder. Therefore, it is an auxiliary diagnostic test method that should be used in conjunction with other clinical and molecular marker tests.

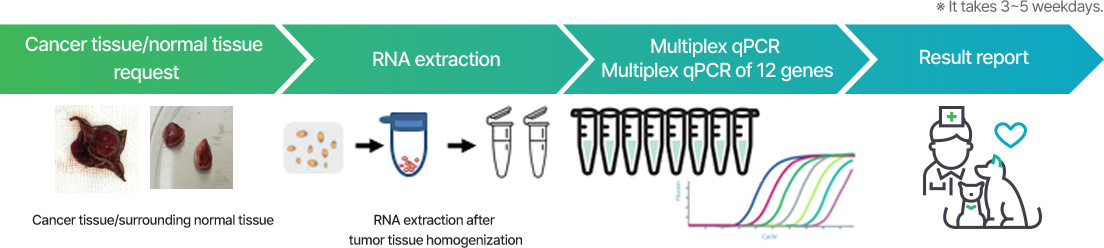
Canine CGE (Cancer Gene Expression) test
This test is a molecular diagnostic test that compares the expression of 12 cancer-related genes, including multiple tyrosine kinase receptors (RTKs), to identify the molecular characteristics of a patient's cancer cells.
Since it is possible to identify overexpressed RTK (Receptor tyrosine kinase) at the RNA level by quantitatively comparing the expression between the patient’s tumor tissue and non-tumor tissue, it can be the basis for using targeted therapies such as specific TKIs (Tyrosine kinase inhibitors).
It can be tested using the same sample when requested along with the chemotherapy response assay, and candidate drugs recommended based on the CGE results can be included in the chemotherapy response assay.
Types of cancer-related genes : VEGFR1, VEGFR2, PDGFR-α, PDGFR-β, EGFR, ErbB2, BRAF, FGFR1, ALK, c-KIT, Vimentin, vWF
Canine CGS (Cancer Gene Sequencing) test
This is a molecular diagnostic test that checks the base sequence of cancer-related genes to identify the molecular characteristics of a patient’s cancer cells.
The presence of mutation of target gene can be checked using DNA extracted from the patient’s cancer cells, which can serve as a basis for using targeted therapeutics such as specific TKIs (Tyrosine kinase inhibitors).
Genes for which sequencing can be performed: KIT, BRAF, KRAS, HER2, EGFR, PIK3CA